Record Low ISS S&P 500 Say on Pay Opposition: The Trends Behind the Decline

In our prior Viewpoint, “Recap of the 2024 Say on Pay Season,” 1 we reported that Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) opposed 7.7% of S&P 500 Say on Pay (SOP) proposals, an unprecedented low. Prior to 2024, ISS opposed about 11% of S&P 500 SOP proposals, on average, each year. In this Viewpoint, the second of our 2024 SOP series, we explore the trends that may have led ISS to recommend against SOP at a historically low rate.
Through careful review of the S&P 500 companies that received 2024 ISS SOP opposition as of August 31, 2024,2 we identified two areas of improvement compared to 2022 and 2023. These changes likely contributed to the overall reduction in 2024 ISS against SOP recommendations.
- Significantly better performance on the ISS Multiple of Median (MOM) test. The MOM test evaluates the ratio of 1-year CEO pay to the median CEO pay of the ISS-selected peer group and has historically been (and continues to be) a meaningful predictor of adverse ISS SOP recommendations. The average MOM outcome was 1.7x in 2024, compared to 2.2x in 2023 and 2.4x in 2022, demonstrating a migration of CEO pay toward peer median levels and fewer outlying pay packages.
- Improvement in Compensation Committee responsiveness to proxy advisor and shareholder concerns over executive pay. We observed fewer Compensation Committees being criticized by ISS for poor responsiveness to shareholder concerns and fewer cases of significant one-time awards that led to an against SOP recommendation. In addition, the number of companies that received ISS opposition to SOP in two consecutive years declined, demonstrating that companies are getting better at addressing investor feedback.
We discuss each area of improvement in detail below.
1. Significantly Better MOM Performance
The three primary ISS quantitative pay for performance (P4P) tests are the Relative Degree of Alignment (RDA) test, the MOM test, and the Pay-TSR Alignment (PTA) test. We examined the distribution of concern levels on each of these three quantitative P4P tests for the companies that received ISS SOP opposition. According to ISS, “Low concern generally indicates long-term alignment between CEO pay and company performance. A Medium concern indicates a moderate misalignment and a High concern indicates a more severe misalignment.” 3
The ISS quantitative P4P tests are highly predictive of ISS SOP recommendations. There is a greater likelihood of ISS SOP opposition when receiving an overall concern level of “High” or “Medium.” In 2024, 71% of the companies that received SOP opposition from ISS scored an overall concern level of “High” or “Medium” on the quantitative P4P assessment. This is similar to the number of companies opposed by ISS that had elevated P4P concern levels in both 2023 (77% of companies) and 2022 (75% of companies).
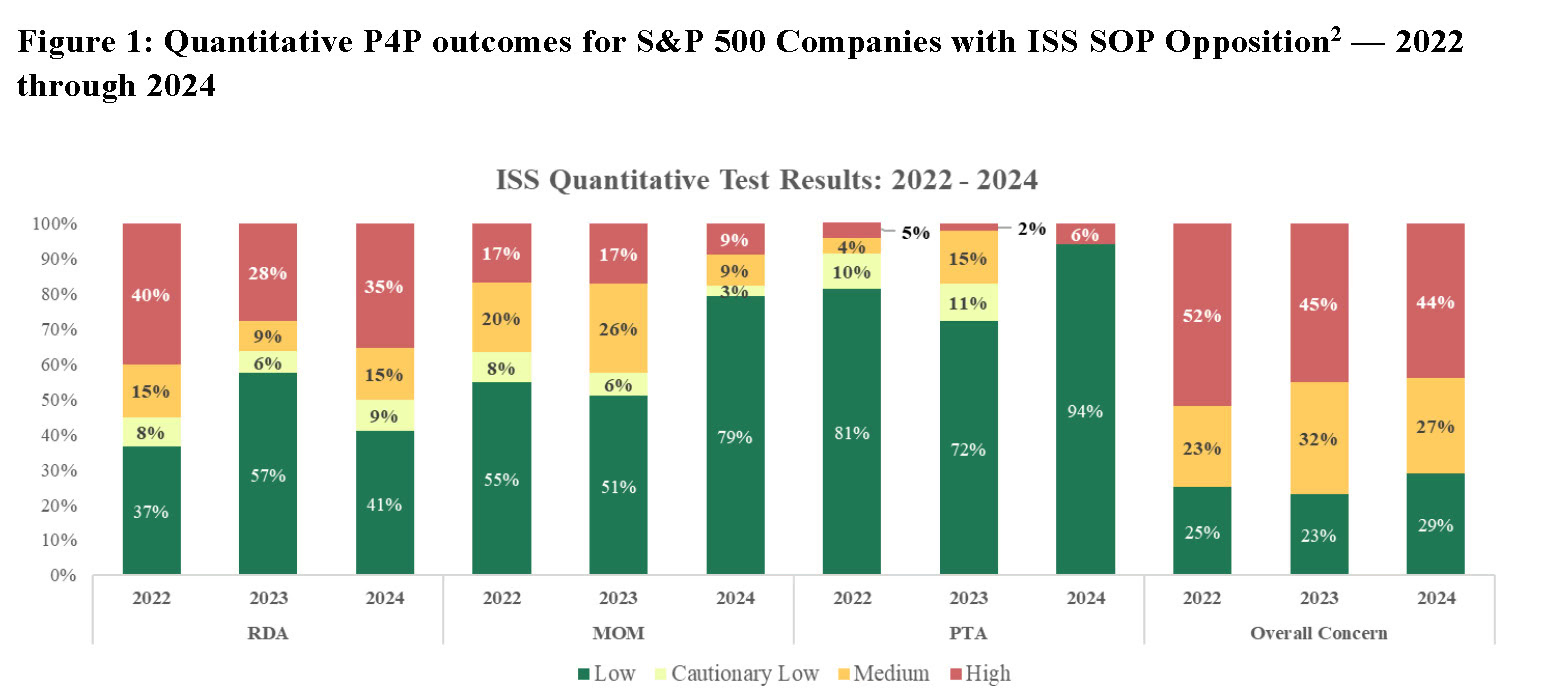
When we examined the individual primary quantitative P4P test outcomes from 2022 to 2024, different patterns emerged. Among companies that received ISS SOP opposition, we observed the greatest improvement in the MOM results. We also observed improvement in PTA results, but most companies continued to receive a “Low” concern. Outcomes of the RDA fluctuated between 2022 and 2024 but generally did not improve. Our conclusions for each of the P4P tests are as follows:
- RDA: measures alignment of 3-year relative CEO pay and 3-year relative TSR. Half of all S&P 500 companies that received SOP opposition from ISS scored a “High” or “Medium” concern on the RDA, showing that RDA outcomes continue to be a primary determining factor of SOP recommendations.
- MOM:evaluates the ratio of 1-year CEO pay to ISS peer median CEO pay.In 2024, only 21% of S&P 500 companies receiving an against SOP recommendation received an elevated concern under the MOM test (an elevated concern is assigned for MOMs that are above 1.69x). This starkly contrasts with 2022 and 2023 results, in which nearly half of all companies opposed by ISS scored an elevated concern on the MOM. Examined another way, the average MOM ratio was 1.7x in 2024, compared to 2.2x in 2023 and 2.4x in 2022. This suggests that CEO pay for FY23 has migrated closer to the median of ISS peers for most companies that were opposed by ISS. In recent years, the MOM test has become increasingly predictive of ISS SOP recommendations. Thus, as companies have shifted their CEO pay quantum towards the “safe middle,” there have been fewer against SOP recommendations overall.
- PTA: measures the absolute alignment of 5-year CEO pay and 5-year indexed TSR. In 2024, nearly all companies (94%) that received SOP opposition from ISS had a “Low” concern on the PTA test. This is an improvement over 2023 and 2022 levels (72% and 81%, respectively) but illustrates a consistent trend that PTA outcomes are not a key driver of SOP recommendations.
2. Improvement in Compensation Committee Responsiveness
In determining its SOP recommendations, in addition to the quantitative P4P tests, ISS conducts a qualitative assessment of executive compensation programs and practices. We compared the qualitative assessments cited in the ISS against SOP recommendations for 2022 through 2024 across six categories. Our objective was to determine if there were significant improvements in the categories over the three years that could have contributed to the decline in adverse SOP recommendations.
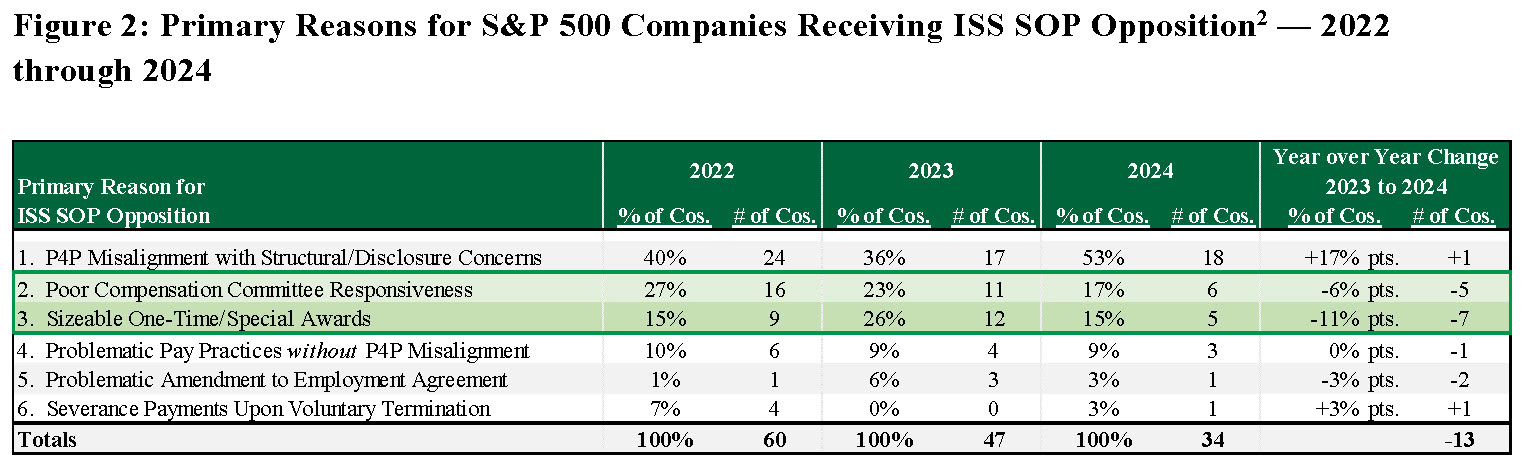
The largest improvements observed in the qualitative reasons for ISS opposition of S&P 500 SOP proposals between 2023 and 2024 were (1) better Compensation Committee responsiveness and (2) fewer sizable one-time/special awards.
- Improved Compensation Committee Responsiveness:Both the percentage and number of companies in 2024 that received ISS SOP opposition primarily due to poor Compensation Committee responsiveness decreased compared to 2023 and 2022 levels. The sustained decline suggests companies continued to take active measures to directly engage with major investors to address their concerns following a SOP proposal that received low support the prior year.
- Reduction in Sizeable One-Time/Special Awards:There was a decrease in the percentage and number of companies that received adverse ISS SOP recommendations due primarily to the grant of special or one-time awards. The practice of granting one-time awards is now strongly disfavored by both proxy advisors and institutional investors. The decline in the use of such awards is consistent with our observation of companies being increasingly responsive to investor and proxy advisor preferences. In addition, the reduction in the use of one-time awards may have contributed to the decrease in “High” and “Medium” concern levels for the MOM test in 2024 — the P4P test focused on 1-year CEO pay quantum.
As another way to evaluate the level of Compensation Committee responsiveness to poor SOP outcomes, we examined the prevalence of consecutive ISS against SOP recommendations. In the 2024 SOP season, the number of companies receiving repeat ISS SOP opposition in two consecutive years (i.e., against in both 2023 and 2024) is tracking below historical levels. The 2022 SOP season featured a historically high 24 companies with against recommendations in consecutive years (or 40% of the total companies opposed by ISS in 2022). The roster of consecutive against recommendations declined significantly in the 2023 SOP season to 13 companies and has further decreased to 9 companies so far in the 2024 SOP season.
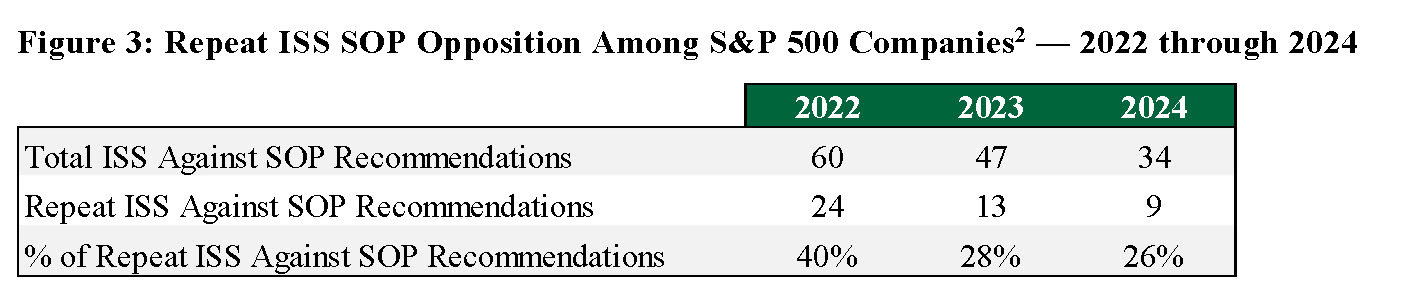
As originally observed in 2023, the continued decline in companies with consecutive ISS SOP opposition demonstrates increased mindfulness of proxy advisor and investor preferences and a willingness to address shareholders’ concerns.
Conclusion
In the 2024 SOP season, we observed a notable decline in ISS opposition of S&P 500 SOP proposals. Based on our review, the main catalysts of the decrease in ISS opposition appear to be (1) improved performance on the MOM quantitative test as CEO pay quantum shifted toward the “safe middle” and (2) continued growth in Compensation Committee responsiveness to proxy advisor and shareholder preferences. In our next Viewpoint in our 2024 SOP series, we will dive into how S&P 500 companies demonstrated responsiveness by examining the actions taken after receiving ISS SOP opposition.
_____________________
1.Perla Cuevas, José Lawani, Linda Pappas, and Olivia Wright. Recap of the 2024 Say on Pay Season. Pay Governance. August 29, 2024. https://www.paygovernance.com/viewpoints/recap-of-the-2024-say-on-pay-season
2.Reflect ISS SOP vote recommendations available through August 31, 2024, collected from ISS Corporate’s Voting Analytics database.
3.Institutional Shareholder Services. United States, Pay-for-Performance Mechanics, ISS’ Quantitative and Qualitative Approach. December 8, 2023. https://www.issgovernance.com/file/policy/active/americas/Pay-for-Performance-Mechanics.pdf?v=2


